Date: 1/5/97
To: Rebecca Wang, EE 275 Graduate Teaching Assistant Department of Electrical Engineering
From: Randy Dimmett
EE 275 A1 Laboratory
Subject: Path of Least Impedance
In this lab, the fact that current flows in the path of least impedance was investigated. It was found that transmission lines (such as coaxial cables) have an impedance that depends on the frequency when they are part of a closed loop. A coaxial cable was connected to a function generator, resistor, and ground strap (between the two ends of the cable). The current was measured through the resistor and strap at various frequencies, holding the voltage source constant.
Appendix I - DC Resistances and Currents Path of Least Impedance
Appendix II
Appendix III - Circuit Model
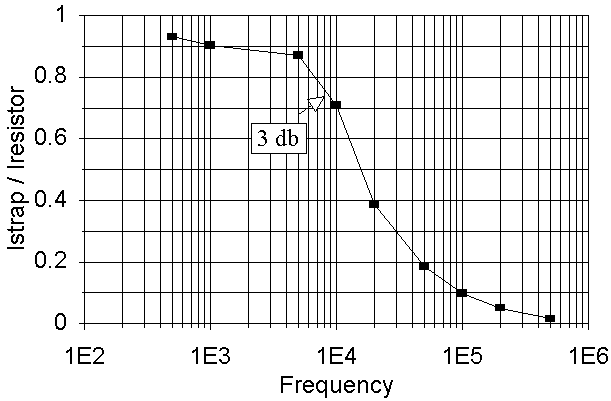
Based on the information gathered in lab, the current will flow more through the ground strap at lower frequencies, and more through the coaxial cable at higher frequencies.
For low frequencies, a resistor can model the coaxial cable. For frequencies below 10000 Hz, the coaxial cable's impedance varies very little (the current varies very little, and the voltage is, of course, constant). After 10 kHz, the current varies too much for the cable to be represented by a resistor. Therefore 10 kHz is the frequency point for which the model has to change for the cable.
Appendix I - DC Resistances and Currents
Path of Least Impedance
DC Resistances
| Inner conductor of coaxial cable: | 8.12 Ohms |
| Outer conductor of coaxial cable: | 8.25 Ohms |
| Ground Strap: | 8.07 Ohms |
| 50 W Nominal Resistor: | 59.01 Ohms |
DC Currents vs. Frequencies
| f (hz) | Istrap (mA) | I-resistor (mA) |
| 500 | 50 | 50 |
| 1000 | 54 | 58 |
| 500 | 56 | 62 |
| 10 K | 54 | 62 |
| 20 K | 44 | 62 |
| 50 K | 24 | 62 |
| 100 K | 11.5 | 62 |
| 200 K | 6 | 61 |
| 500 K | 3 | 60 |
| 1 M | 1 | 60 |
Appendix II
Path of Least Impedance
Plot of Istrap / Iresistor vs. Frequency

Appendix III - Circuit Model
Path of Least Impedance
Circuit Model:
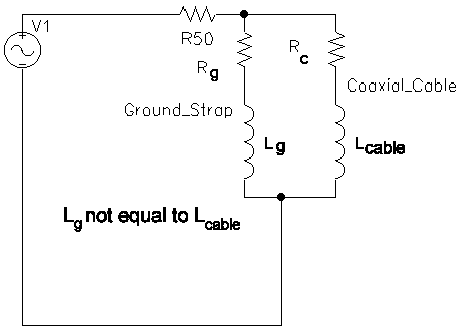
Iground strap = Iresistor * (Rc + jwL)/(Rc + jwL + Rg) (Current Divider)
Therefore, Iground strap/ Iresistor = (Rc + jwL)/(Rc + jwL + Rg)
Therefore, Iground strap * (Rc + jwL + Rg) = Iresistor * (Rc + jwL)
Therefore, (Iground strap - Iresistor) * jwL = (Iresistor - Iground strap) * Rc - Iground strap * Rg
Therefore, w = [-Rc - (Iground strap * Rg)/ (Iground strap - Iresistor) ] / (j * L)
Therefore, w = j * [Rc + (Iground strap * Rg)/ (Iground strap - Iresistor) ] / L
Therefore, | f | = 2*p / |w| = 2*p*L / [Rc + (Iground strap * Rg)/ (Iground strap - Iresistor) ]